What is DOE?
In general usage, design of experiments (DOE) or experimental design is the design of any information-gathering exercises where variation is present, whether under the full control of the experimenter or not. However, in statistics, these terms are usually used for controlled experiments. Design of experiments (DOE) is a series of tests in which purposeful changes are made to the input variables of a process so that we may observe and identify corresponding changes in the output response.
It is a valuable tool to optimise product and process designs, accelerate the development cycle, reduce development costs, improve the transition of products from research and development to manufacturing and effectively troubleshoot manufacturing problems. Today, the Design of Experiments is viewed as a quality technology to achieve product excellence at the lowest possible overall cost.
Purpose of Experimentation
Comparing Alternatives. It helps us to compare two or more alternatives and choose the best one. For instance, choose the best vendor who supplies the raw material.
Determining which input variables are most influential on the output or response variable. For example, what are the significant factors amongst raw material, temperature, process time, operator and etc.?
Determining where to set the influential controllable input variables so that output is near the nominal requirement. For instance, If temperature is the most influential factor, what is the temperature which results in the best quality product.
Determining where to set the influential input variables so that variability in the response variable is small.
Determining where to set the influential input variables so that the effects of the input variables which are out of our control are minimised.
Benefits of DOE
A typical experiment that is usually used to show the advantage of DEO is called the Catapult experiment. The main questions in this experiment are that how far does the catapult throw the ball? How can we adjust the catapult to hit a target? Which one is more important? Stop angle, Rubberband tension, hook, …?
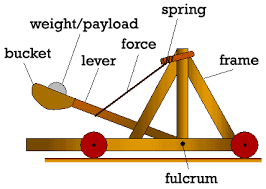
As a result of a simple DOE, it is reported that it took about 200 man-hours and the experimental results showed that predicting the ball landing site was accurate within 15 inches, whereas the design of the experiment approach requires 6 man-hours and it was accurate within 3 inches. It shows how DOE can save resources to hit the target sooner, more precise, and more efficient.
Implementation
The main steps to implement an experimental design are as follows.
- Define problem statement and experimental objectives. For example, an aircraft manufacturer is interested to maximise paint adhesion to aluminium surface of aircraft. Different primer paints and painting methods are considered to find the best solution.
- Select the output (Response) variable. As the output variable, a finished paint was applied and the adhesion force was measured.
- Select the input variables (factors) and their levels. For instance, Painting Method with levels “dipping” and “spraying” and primer type with types 1, 2and 3.
- Select the experimental design such as Full factorial design, fractional factorial design, Taguchi design by considering sample size (number of replicates), the selection of a suitable run order for the experimental trials, the criticality of errors and etc.
- Execute the experiment and collect data. It is important to use a data collection form to collect the data and make notes of observations, other factor settings, etc. during the experiment.
- Analyse the data and draw statistical and practical conclusions using different statistical software such as Minitab
- Validate the statistical conclusion in a practical situation by setting the process inputs at the practical results and see if the process output responds as expected.
- Document and summarise the results and conclusions, in tabular and graphical form, for the report or presentation on the study.
How CBIS can help you
Please contact us if you need more details on how our expert team can assists you in training and implementation of DOE and lean six sigma projects.
What is DFSS? Design for Six Sigma is used to perfect products and processes before...
What is coaching? Coaching is a cyclical process of elevating the other persons’ awareness of...
Introduction In our lean six sigma projects, too often we spend all our time on...
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful method for improving existing products, processes and services. One...
As global competition continues to grow, the pressure to improve becomes more and more intense....
What is SMED? SMED is the term used to represent setup time and is often...
Lean Six Sigma projects can lead to a rewarding experience and immense benefits for an...
Introduction Value Stream Map (VSM) is a diagram of every step involved in the material...
Attending our Public classroom physically or joining the team virtually from anywhere, according to the training calendar.
A flexible self-paced training for busy people along with our support by a dedicated coach, to solve the disadvantage of one-way online training
Delivering flexible and tailored training for your team and at your premises as a cost-effective solution for your team.










